Digital Modes Interfaces
SWISSLOG interfaces with the following digital modes programs:
- MULTIMODE:
- MIXW: (www.mixw.net)
- FLDIGI (www.w1hkj.com)
- MultiPSK (http://f6cte.free.fr)
- TrueTTY (www.dxsoft.com/en/products/truetty)
- Hamscope (www.qsl.net/hamscope): Although HamScope is an old program, it’s very useful because it uses the very popular MMTTY engine by JE3HHT for RTTY (http://hamsoft.ca/pages/mmtty.php). You can work AFSK but also FSK by using the EXTFSK.DLL extension. There is also an enhanced EXTFSK64.DLL available in http://www.qsl.net/ja7ude/extfsk/indexe.html. It’s the best way to use MMTTY along with Swisslog! Please visit the HamScope and MMTTY website for more details.
- Digital Master 780 (DM780) (https://www.hamradiodeluxe.com/) Included in Ham Radio De Luxe.
- JT65/FT8/FT4:
- WSJT-X (https://physics.princeton.edu/pulsar/k1jt/wsjtx.html)
- JTDX (http://www.jtdx.tech)
- MSHV (http://lz2hv.org/mshv)
- JT65-HF HB9HQX-Edition (https://sourceforge.net/projects/jt65hfhb9hqxedi)
- SPECIAL MODES:
- SIM PSK (http://www.sim.on2vhf.be)
- JS8Call (https://groups.io/g/js8call)
- VarAC (https://www.varac-hamradio.com/)
- MMSSTV YONIQ (http://radiogalena.es/yoniq/) Version 1.13.2 Alpha or higher required.
- N1MM (https://n1mmwp.hamdocs.com/) Contest software
FLDIGI, HamScope, WSJT-X, JTDX, MSHV, JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition, SIM PSK, N1MM and JS8 CALL are FREE. MultiPSK is freeware but you need to buy a license to get some auxiliary functions. MixW, DM780 and TrueTTY need registration.
It allows to work digital modes in real time from these programs and save the QSO in Swisslog at the same time.
From Multimode programs (except DM780), QSO Data are sent automatically to SWISSLOG in the following ways:
- when the focus leaves the field (MixW and HamScope)
- the field content is updated (FLDIGI and MultiPSK)
- by using the pop-up menu of the digital modes program.
In HamScope Call and Name are sent from SWISSLOG when a Call is entered into the QSO-Edit View of SWISSLOG
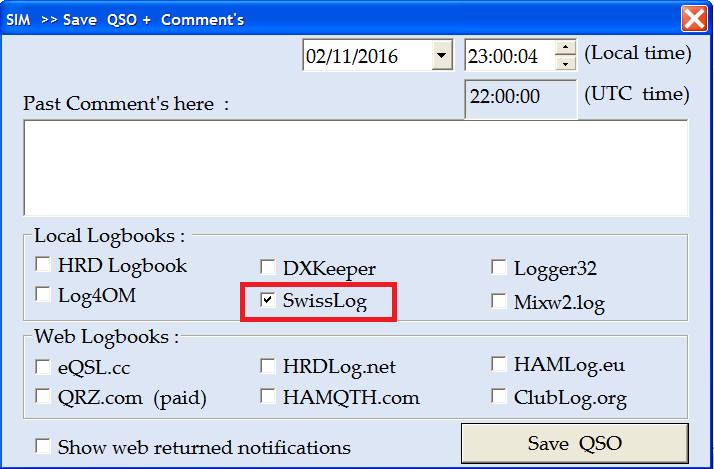
In DM780, N1MM, SIM PSK, VarAC and MMSSTV YONIQ when user press the corresponding Save QSO button, all QSO data is transferred to Swisslog and QSO is saved automatically.
For WSJT-X, JTDX, MSHV and JS8Call please read the specific section later.
Setup the Digital Modes Support in SWISSLOG
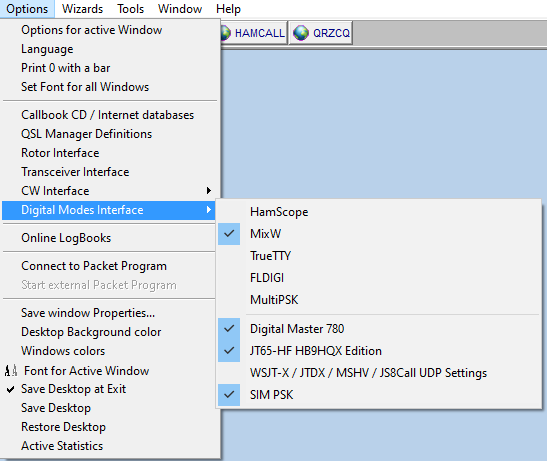
- Select the menu item Options | Digital Modes-Interface and then the program you will be using:
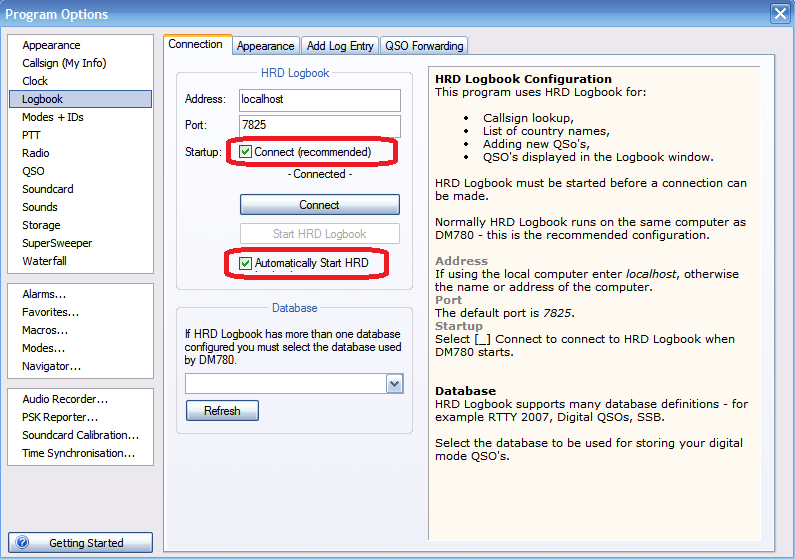
- Digital Master 780, N1MM, JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition and SIM PSK don't need any further setup in Swisslog. You have to select the program you want to enable direct logging (you can check more than one). WSJT-X / JTDX / MSHV / JS8Call need additional setup. Please read the operation section for the selected programs.
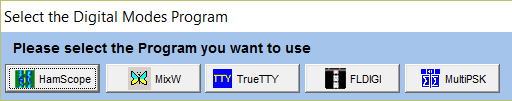
- ONLY applicable for Multimode programs (except DM780): if you have
not configured previously Multimode programs, the first time you press the
![]() button
located at the bottom of the QSO entry window, Swisslog will prompt you to
select the Multimode program you will
be using:
button
located at the bottom of the QSO entry window, Swisslog will prompt you to
select the Multimode program you will
be using:
Options ONLY for Multimode programs (except DM780)
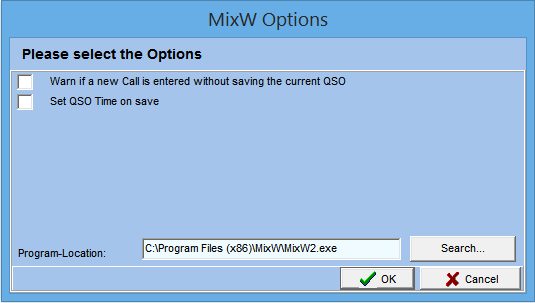
- The following Dialog is displayed if you select MixW, FLDIGI or MultiPSK :
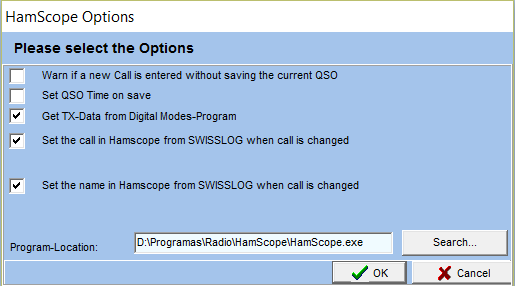
- The following Dialog is displayed if you select Hamscope:
- When selecting TrueTTY a dialog is displayed where you have to specify the directory in which TrueTTY.Exe is located.
The options are the following:
- Warn if a new Call is entered without saving the current QSO: when you enter a callsign in the Digital Modes program automatically is entered (not saved) in the QSO entry window of Swisslog. If you change the callsign in the Digital Mode program without saving the current QSO you can release a warning message in Swisslog. By default this option is not checked and it's recommended for a better operation. This way you have all the Save/Delete control in the digital modes program without any warning messages from Swisslog.
- Set QSO Time on save: Check this option if you want the QSO Time to be set to the time when you press the Save QSO button in the digital modes program. If unchecked (default option) the behaviour is the following: the QSO Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will be set when you press the Save QSO button.
- Get TX-Data from Digital Modes-program: Check this option if you want to control your transceiver from the Digital Modes program.
- Set the call in HamScope from SWISSLOG when a call is changed: check this option if you want to set the callsign in Hamscope when you change it from SWISSLOG.
- Set the name in HamScope from SWISSLOG when a call is changed: check this option if you want to set the operator name in Hamscope when you change it from SWISSLOG.
- Program-Location: enter (or search) the full path and name of the digital modes program.
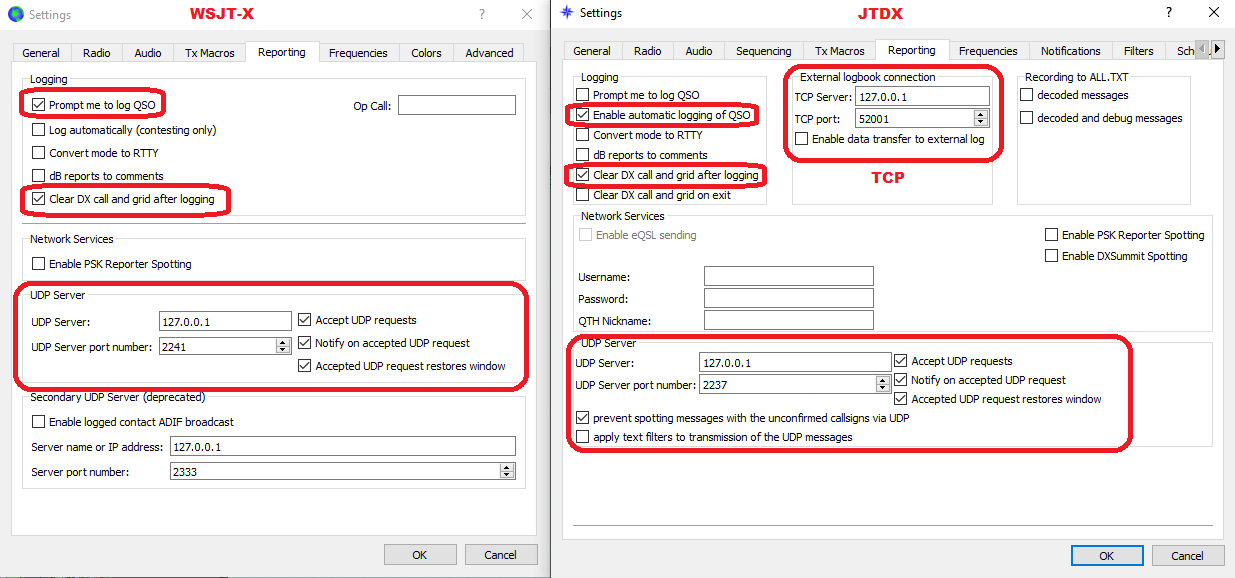
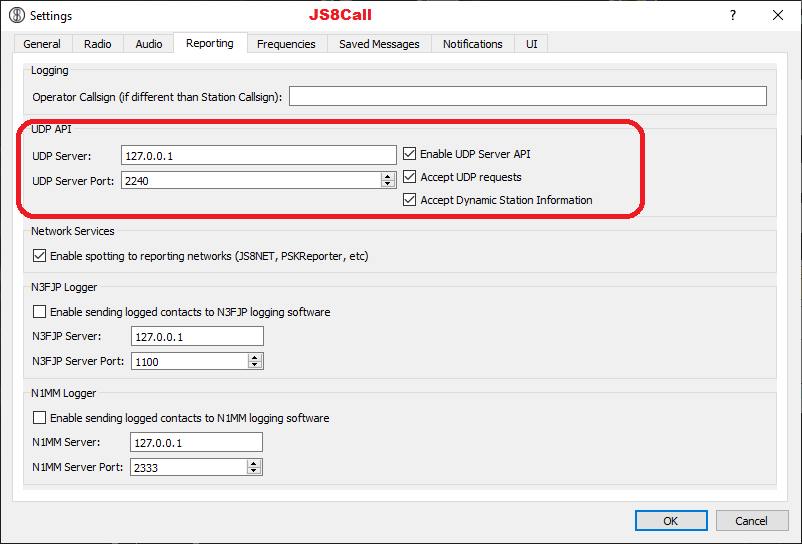
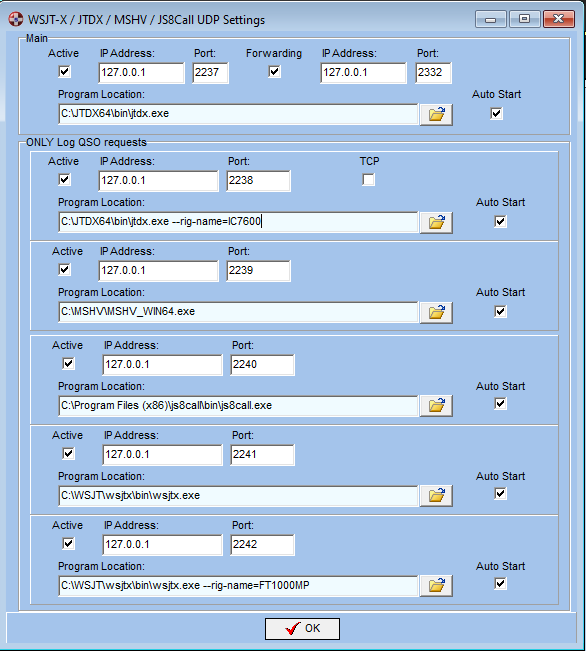
WSJT-X / JTDX / MSHV / JS8Call UDP Settings
Swisslog supports up to 6 different instances of these programs running at the same time! There are 2 different ways to configure them:
- MAIN: program configured in this section will be used
to be linked with the QSO entry window and to display the band activity in
the WSJT-X / JTDX band maps. Please
note that band activity is
only sent by WSJT-X / JTDX! MSHV and JS8Call don't send
this information.
I suggest to use WSJT-X or JTDX as main instance and MSHV and JS8Call in the
Log QSO Requests section (see below).
When Swisslog receives the first UDP packet from this "main" instance, the UDP button is displayed in green colour:
 This indicates that Swisslog is linked via UDP with the program
defined here. Press
this button again to disable the link with the "main" instance. It will
be displayed like this:
This indicates that Swisslog is linked via UDP with the program
defined here. Press
this button again to disable the link with the "main" instance. It will
be displayed like this:
 .
.Callsign found or manually typed in the "DX Call" field will be automatically entered (not saved) in the QSO Entry window of Swisslog. Mode and Grid are also transferred. This is very useful to avoid using any external program for dupe checking (i.e.: JTALERT). At the same time, you get all the benefits of Swisslog to retrieve callbook or membership information, statistics, etc. To clear the callsign in Swisslog perform one of the following actions, according the program to be used:
- WSJT-X: Instead of deleting character by character, select the full callsign in the "DX Call" field and press the Delete key of your keyboard to clear all the field at once.
- JTDX: Press the "Clear DX" button
- MSHV: Press "Reset QSO"
NOTE: Avoid typing manually a callsign in the "DX Call" field! Callsign begins to be transferred to Swisslog when callsign in the DX Call field contains 3 or more characters (minimum callsign length). However, every time you add/delete a new character to the call it's transferred again to the QSO Entry window as if it was a new callsign (there is no need to press the Enter key to send the field content). For this reason, you may experience some delay in getting all the information about the callsign, because Swisslog has to process "several" callsigns in a very short time until you finish to type the full callsign.
It's important to know that WSJT-X / JTDX sends status messages very often when various internal states changes. These messages allow Swisslog to synchronise the content of the DX Call field and current mode of operation. This is perfect when you want to work with WSJT-X or JTDX. However, if you want to manually enter callsigns in Swisslog or work other modes with MixW, FLDIGI, etc. (linked with Swisslog) while WSJT-X / JTDX is running and the UDP link is enabled, you have to disable the link by pressing the UDP button. Otherwise you will go crazy because Swisslog will always follow the callsign/mode set in WSJT-X / JTDX ignoring other inputs.
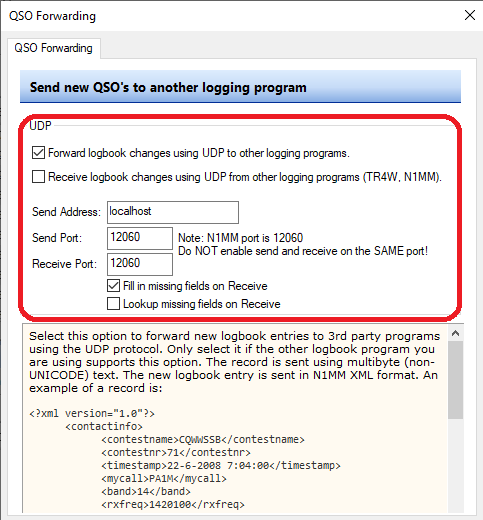
- ONLY Log QSO requests: Swisslog will only accept "Log QSO" requests from programs defined in this section. You can define up to 5 different instances. This is very useful for multioperator stations or stations having different radios working in different bands at the same time with different instances of WSJT-X / JTDX / JS8Call or working MultiSlot with MSHV. IMPORTANT: if you plan to use MSHV and its MultiSlot feature, you must configure it in this section, NOT as Main!
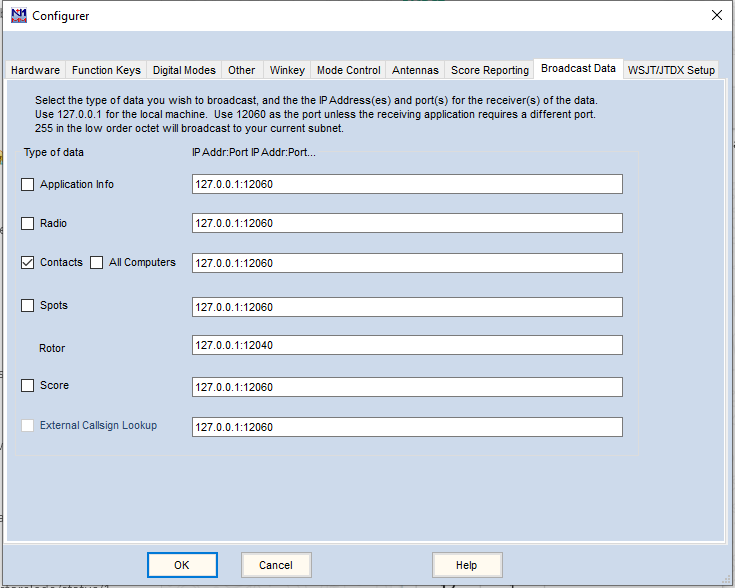
Go to Options | Digital Modes-Interface > WSJT-X / JTDX / MSHV / JS8Call UDP Settings:
- Set the following options in every section:
- Active: Check this option to enable this instance
- IP Address: set here the IP address defined in the selected program. By default is 127.0.0.1
- Port: set here the UDP port used by the selected program. By default is 2237. VERY IMPORTANT: you have to define a different port on every program or different instance of the same program!
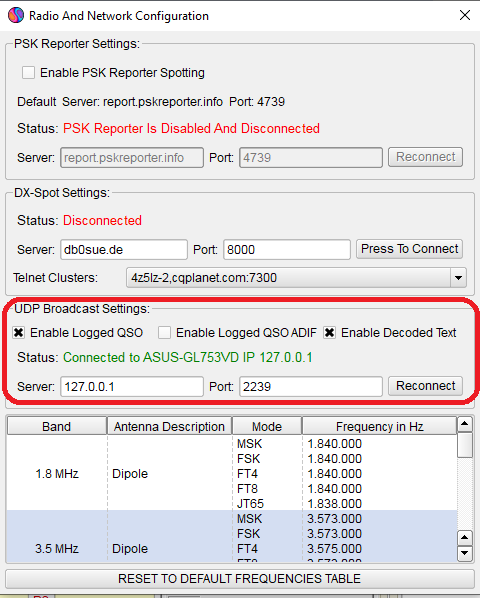
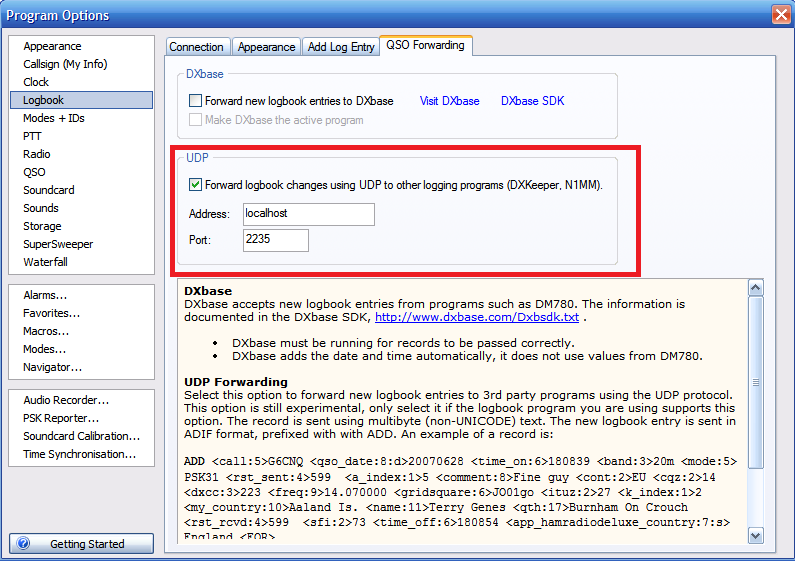
- Forwarding: check this option to allow Swisslog forward received UDP messages to third party programs (such Grid Tracker by N0TLL) in the selected IP / port address. If using Grid Tracker, go to Settings > General > Receive UDP messages then set the forwarding port (2332 by default but you can use whatever you know it's free).
- Program location: type or search the full path and name of the program to be used. Remember that multiple instances of WSJT-X / JTDX / JS8Call needs unique rig names! In order to create a new instance of a same program simply add --rig-name=RIGNAME at the end of the full path and name (see the screenshot below).
- Auto Start: check this option if you want to start automatically the selected program when Swisslog starts up.
- TCP: check this option to receive logging QSO requests from programs using the N1MM TCP data format. For example: JTDX, VarAC, GreenCube Terminal or MMSSTV YONIQ. Default port is 52001. IMPORTANT: Although this method is available for JTDX (using its TCP Server), I highly suggest to use the UDP connection which offers better features.
| SPECIAL NOTE FOR JTALERT USERS |
|
If you want to use JTALERT along with Swisslog and WSJT-X or JTDX you have to use JTALERT version 2.10.17 or higher which supports UDP packet rebroadcasting on an user defined IP & Port. This must be done because the UDP port can't be shared by 2 applications at the same time. Perform the following steps if you want to use JTALERT along with Swisslog and WSJT-X / JTDX:
|
In case of communication problems check that your antivirus/firewall is not blocking any of the selected UDP/TCP ports!
Important about transceiver control
Because nearly all digital modes are worked in USB or LSB (except RTTY if you work in FSK), if we are using the transceiver CAT control in Swisslog, we don't want that QSO are saved in the transceiver mode but in the real mode of operation. We also want to save the REAL frequency of operation of the digital mode being used and not the frequency displayed in the transceiver which is the USB/LSB frequency. MixW and FLDIGI sends the real frequency of operation and this is very interesting. For these reasons when the link is established between Swisslog and all supported digital modes programs (except TrueTTY) the transceiver control in Swisslog is stopped automatically giving full CAT control to these programs. For a proper operation, you have to setup the transceiver control in these programs. When deactivating the link the transceiver control in Swisslog will be started again (only if you set the option to start automatically the transceiver control).
![]() IMPORTANT: Hardware
serial COM ports
can't be opened by two programs simultaneously. If you deactivate the link
between the digital modes program and Swisslog, you
will get an error when restoring the CAT control in Swisslog because the
digital modes program is
still running and using the COM
port. If you are using a commercial interface (such as MicroHam) read the
documentation because some of them bring the possibility to setup 2 or more
serial ports to be used as CAT control. If you don't have this option or you
are using a regular CAT cable or interface there is an excellent solution
available to solve this
problem! Virtual Serial Port Emulator (VSPE) software allows you to
split your hardware serial COM ports into virtual serial ports which can be used
with up to 4 programs simultaneously! It's a perfect solution to control
your transceiver, PTT port, or rotator simultaneously in several programs. It also offers some other interesting
functions. Best of all: it's free for 32 bits operating systems and it cost
around $25 for 64 bits platforms. Please visit
http://www.eterlogic.com/Products.VSPE.html to download it and get
further information.
IMPORTANT: Hardware
serial COM ports
can't be opened by two programs simultaneously. If you deactivate the link
between the digital modes program and Swisslog, you
will get an error when restoring the CAT control in Swisslog because the
digital modes program is
still running and using the COM
port. If you are using a commercial interface (such as MicroHam) read the
documentation because some of them bring the possibility to setup 2 or more
serial ports to be used as CAT control. If you don't have this option or you
are using a regular CAT cable or interface there is an excellent solution
available to solve this
problem! Virtual Serial Port Emulator (VSPE) software allows you to
split your hardware serial COM ports into virtual serial ports which can be used
with up to 4 programs simultaneously! It's a perfect solution to control
your transceiver, PTT port, or rotator simultaneously in several programs. It also offers some other interesting
functions. Best of all: it's free for 32 bits operating systems and it cost
around $25 for 64 bits platforms. Please visit
http://www.eterlogic.com/Products.VSPE.html to download it and get
further information.
NOTE: If you are using MixW, WSJT-X, JTDX, MSHV, JS8Call, JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition or SIM PSK you can avoid using VSPE by using OmniRig as CAT control in these programs and Swisslog. If you are using FLDIGI you can select FLRIG for CAT control in FLDIGI and Swisslog. Please read the transceiver control chapter.
Activate/ Deactivate Multimode programs
To activate the selected Multimode program (except Digital Master 780) press the button in the QSO Edit Window. Depending your selection it will be displayed as:
- For MixW:

- For FLDIGI:
![]()
- For MultiPSK:
![]()
- For HamScope:
![]()
- For TrueTTY: ![]()
The red indicator tells you that Swisslog is not linked to the digital modes program. Pressing this button starts the selected digital modes program (if the program was not running before the execution of Swisslog) and enables the link to it. When the link is established you will see a green indicator. You can press again this button if you want to deactivate the link between both programs (this works this way in all programs except for TrueTTY).
IMPORTANT: While the link is established with the selected Multimode program (green button) the X button to close the QSO entry window will be disabled (except for TrueTTY). The QSO Entry window must be open during the link. Press the digital mode button to deactivate the link if you need to close the QSO Entry window.
MixW Operation
To start operating digital modes linking Swisslog with MixW you have to
press the button
 . MixW will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
. MixW will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
 . The green
dot indicates that the DDE link has been established between Swisslog and
MixW. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close MixW Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between MixW and Swisslog.
. The green
dot indicates that the DDE link has been established between Swisslog and
MixW. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close MixW Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between MixW and Swisslog.
Deactivating the link by pressing the
 button can be
very useful in the following cases:
button can be
very useful in the following cases:
- you prefer to work SSB in Swisslog using the CAT functions of the DX Window but don't want to close MixW
- you are editing QSO in MixW and don't want that MixW sends data to Swisslog while editing
- you are working digital modes but alternating with SSB/CW in Swisslog and this option gives you more flexibility and fast changes to operate from one program to another
When you enter a callsign in MixW automatically will be entered (not saved) in the QSO Entry window of Swisslog. You can enter a callsign in MixW in 3 different ways:
- Manually entering a callsign and press Enter or change cursor to another field
- Double click on the received Callsign in the RX window
- Selecting a Callsign in the RX window, mouse right click and select "Call"
Swisslog reads from the following MixW fields:
- Callsign
- Mode
- QSO Frequency (real frequency of operation)
- RST sent
- RST received
- Name (operator)
- QTH
- Notes
- QSL manager
- QTH Locator
- State
- County
- IOTA
If you change the contents in any of the above fields in MixW, Swisslog will transfer the contents automatically to the corresponding fields. Because the QSL manager field of MixW may contain different information than a QSL manager callsign, Swisslog will extract the first valid callsign found in this field.
Keep also in mind that when entering the State or County in MixW it must have the same format as Swisslog recognises (which is the standard format), otherwise you will create wrong entries in your WAS o US Counties statistics. The US State has 2 letters: PA, NY, MD, WA, etc. The US County has de following format: US State - County name. i.e. NY-ALBANY, PA-WASHINGTON. Swisslog DOESN'T check the validity of the transferred data!
Name and QTH Locator fields will be checked in the selected Callbook databases in Swisslog (if configured). Name will only be checked if empty in MixW. If QTH locator is set as 4 digit format in MixW and found in Callbook databases in 6 digits format (same Maiden Head!), the 6 digits locator will be saved in Swisslog. Example:
-
JN93 is set in MixW for current QSO. After checking in the selected Callbook database, Swisslog find a profile for this station with locator JN93AL. JN93AL will be saved in QSO instead of JN93.
Swisslog recognises all the MixW modes except FSK63 and FSK125 which are not LOTW/ADIF compliant. If used they are converted to FSK31.
If you press the MixW button
![]() the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and MixW. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and MixW. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
![]() .
.
If you press the MixW button
![]() all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and MixW. Keep in mind that if you select any saved QSO
in MixW (i.e. for editing) you will see that Swisslog enters the callsign as
if it were a new QSO (calm! it's entered not saved!). This is a normal
behaviour because MixW sends the selected callsign via DDE link the same way
as if it were a new QSO. Swisslog is not able to know if you are editing
or entering a new QSO. If you are editing QSO in MixW a good choice is
deactivating temporally the link by pressing the
all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and MixW. Keep in mind that if you select any saved QSO
in MixW (i.e. for editing) you will see that Swisslog enters the callsign as
if it were a new QSO (calm! it's entered not saved!). This is a normal
behaviour because MixW sends the selected callsign via DDE link the same way
as if it were a new QSO. Swisslog is not able to know if you are editing
or entering a new QSO. If you are editing QSO in MixW a good choice is
deactivating temporally the link by pressing the
 button. If you set the cursor to the new QSO line in MixW
you may press the button
button. If you set the cursor to the new QSO line in MixW
you may press the button
![]() to clear the
QSO fields in both MixW and Swisslog. Or you can press the Cancel button in
Swisslog to clear the QSO entry fields of Swisslog.
to clear the
QSO fields in both MixW and Swisslog. Or you can press the Cancel button in
Swisslog to clear the QSO entry fields of Swisslog.
FLDIGI Operation
To start operating digital modes linking Swisslog with FLDIGI you have to
press the button
![]() .
FLDIGI will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
.
FLDIGI will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
![]() . The green
dot indicates that the link has been established between Swisslog and
FLDIGI. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close FLDIGI Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between FLDIGI and Swisslog.
. The green
dot indicates that the link has been established between Swisslog and
FLDIGI. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close FLDIGI Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between FLDIGI and Swisslog.
Deactivating the link by pressing the
![]() button can be
very useful in the following cases:
button can be
very useful in the following cases:
- you prefer to work SSB in Swisslog using the CAT functions of the DX Window but don't want to close FLDIGI
- you are working digital modes but alternating with SSB/CW in Swisslog and this option gives you more flexibility and fast changes to operate from one program to another
When you type a callsign in FLDIGI automatically will be entered (not saved) in the QSO Entry window of Swisslog. You can enter a callsign in FLDIGI in 2 different ways:
- Manually entering a callsign in the Call field (see note below)
- Selecting a Callsign in the RX window (right to left), mouse right click and select "Call"
NOTE: Content of FLDIGI QSO fields are transferred inmediately to the corresponding fields in Swisslog while typing in any QSO field (there is no need to press the Enter key to send the field content). By using this method there is no way to know when user has finished to enter a full callsign! Callsign begins to be transferred to Swisslog when callsign in FLDIGI contains 3 or more characters (minimum callsign length). However, every time you add/delete a new character to the call it's transferred again to the QSO Entry window as if it was a new callsign. For this reason you may experience some delay in getting all the information about the callsign, because Swisslog has to process "several" callsigns in a very short time until you finish to type the full callsign. To avoid this behaviour I recommend to use the second method described above because the full callsign is sent to Swisslog in one go (see screenshot below):
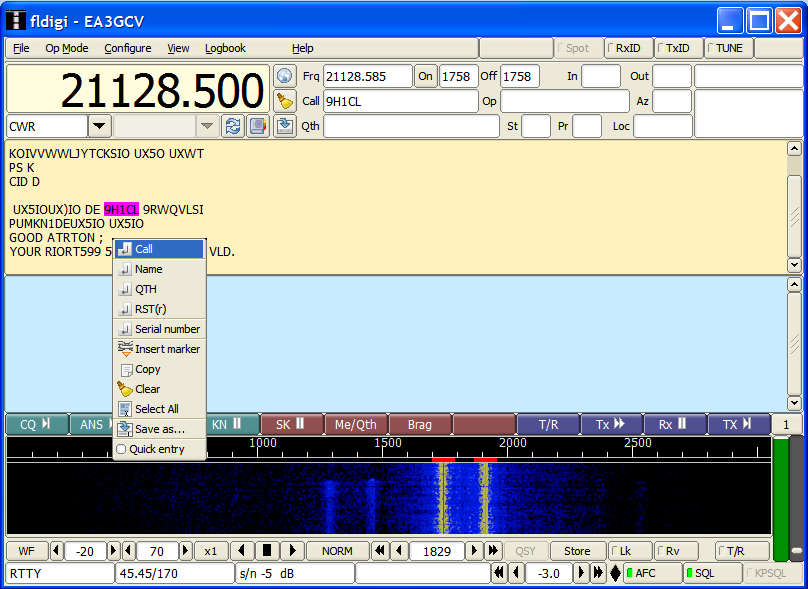
Swisslog reads from the following FLDIGI fields:
- Call
- Op Mode
- Frq (real frequency of QSO)
- Out (RST sent)
- In (RST received)
- #R (Serial number received in contest, RSTR_NR)
- Op (Operator)
- QTH
- Loc (QTH Locator)
- St (US State)
- Notes
If you change the content in any of the above fields in FLDIGI, it will be transferred automatically to the corresponding field in Swisslog.
Keep also in mind that when entering the US State in FLDIGI it must have the same format as Swisslog recognises (which is the standard format), otherwise you will create wrong entries in your WAS award. The US State has 2 letters: PA, NY, MD, WA, etc. Swisslog DOESN'T check the validity of the transferred data!
Name and Locator fields will be checked in the selected Callbook databases in Swisslog (if configured). Name will only be checked if empty in FLDIGI. If QTH locator is set as 4 digit format in FLDIGI and found in Callbook databases in 6 digits format (same Maiden Head!), the 6 digits locator will be saved in Swisslog. Example:
-
JN93 is set in FLDIGI for current QSO. After checking in the selected Callbook database, Swisslog find a profile for this station with locator JN93AL. JN93AL will be saved in QSO instead of JN93.
If you press the FLDIGI button
![]() the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and FLDIGI and at the same time will clear
all QSO fields in FLDIGI. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and FLDIGI and at the same time will clear
all QSO fields in FLDIGI. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
![]() .
.
If you press the FLDIGI button
![]() all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and FLDIGI.
all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and FLDIGI.
IMPORTANT: If you use the eQSL realtime logging option in Swisslog you have to disable the eQSL realtime logging in FLDIGI, otherwise you will upload 2 QSOs at the same time!
MultiPSK Operation
Before using MultiPSK together with Swisslog, you have to activate an option in the MultiPSK configuration. Swisslog reads data from MultiPSK by using the TCP/IP link of MultiPSK and also from the internal DDE server. By default the TCP/IP link is not active. To activate it start MultiPSK and go to the configuration screen, select "Your logbook" and select the option "TCP/IP client Logbook (through the Multipsk TCP/IP link"):
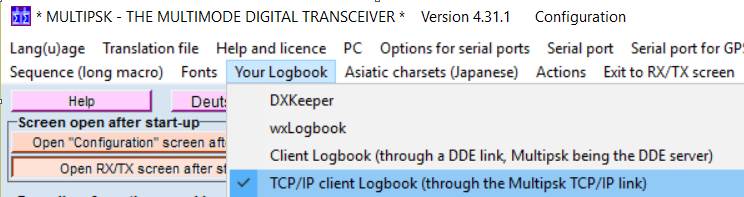
Now you are ready to start operating digital modes linking Swisslog with MultiPSK.
Press the button
![]() .
MultiPSK will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
.
MultiPSK will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
![]() . The green
dot indicates that the TCP/IP link has been established between Swisslog and
MultiPSK. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close MultiPSK Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between MultiPSK and Swisslog.
. The green
dot indicates that the TCP/IP link has been established between Swisslog and
MultiPSK. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close MultiPSK Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between MultiPSK and Swisslog.
Deactivating the link by pressing the
![]() button can be
very useful in the following cases:
button can be
very useful in the following cases:
- you prefer to work SSB in Swisslog using the CAT functions of the DX Window but don't want to close MultiPSK
- you are working digital modes but alternating with SSB/CW in Swisslog and this option gives you more flexibility and fast changes to operate from one program to another
When you type a callsign in MultiPSK automatically will be entered (not saved) in the QSO Entry window of Swisslog. You can enter a callsign in MultiPSK in 2 different ways:
- Manually entering a callsign in the Callsign field (see note below)
- Selecting a Callsign in the RX window, mouse right click and select "Call"
NOTE: Content of MultiPSK QSO fields are transferred inmediately to the corresponding fields in Swisslog while typing in any QSO field (there is no need to press the Enter key to send the field content). By using this method there is no way to know when user has finished to enter a full callsign! Callsign begins to be transferred to Swisslog when callsign in MultiPSK contains 3 or more characters (minimum callsign length). However, every time you add/delete a new character to the call it's transferred again to the QSO Entry window as if it was a new callsign. For this reason you may experience some delay in getting all the information about the callsign, because Swisslog has to process "several" callsigns in a very short time until you finish to type the full callsign. To avoid this behaviour I recommend to use the second method described above because the full callsign is sent to Swisslog in one go (see screenshot below):
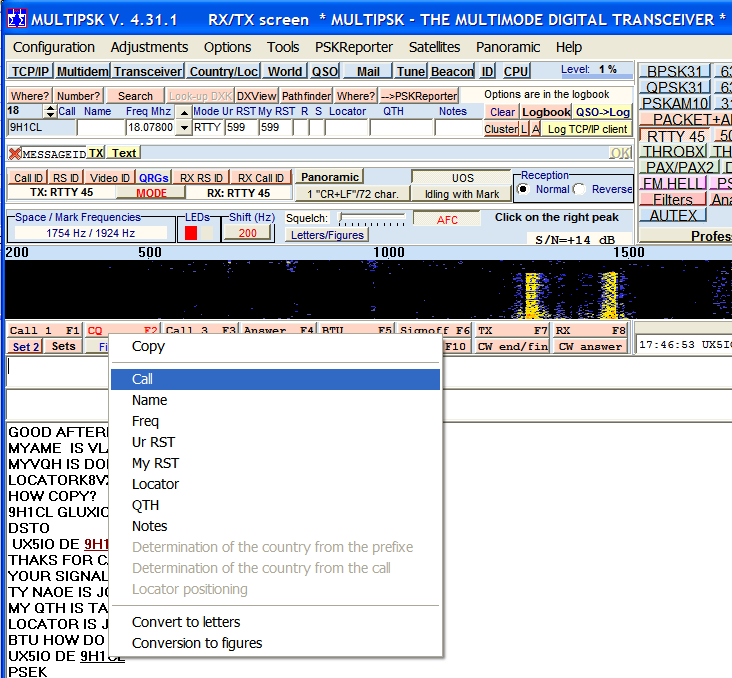
Swisslog reads from the following MultiPSK fields:
- Call
- Name (Operator)
- Freq
- Mode
- Ur RST (RST sent)
- My RST (RST received)
- Locator
- QTH
- Notes
If you change the content in any of the above fields in MultiPSK, it will be transferred automatically to the corresponding field in Swisslog.
Name and Locator fields will be checked in the selected Callbook databases in Swisslog (if configured). Name will only be checked if empty in MultiPSK. If QTH locator is set as 4 digit format in MultiPSK and found in Callbook databases in 6 digits format (same Maiden Head!), the 6 digits locator will be saved in Swisslog. Example:
-
JN93 is set in MultiPSK for current QSO. After checking in the selected Callbook database, Swisslog find a profile for this station with locator JN93AL. JN93AL will be saved in QSO instead of JN93.
Swisslog recognises all the MultiPSK except the professional modes and the following special modes: ASCII, LENTUS, ALE400 and 141A (ALE). If using any of these modes user will have to manually select any similar QSO mode in Swisslog or add them in Edit | Add / Edit modes.
If you press the MultiPSK button
![]() the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and MultiPSK. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
the QSO
will be saved in both Swisslog and MultiPSK. If you set the Set QSO Time
on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press
the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO
Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will
be set when you press the button
![]() .
.
If you press the MultiPSK button
![]() all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and MultiPSK.
all QSO
fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and MultiPSK.
TrueTTY Operation
To start operating digital modes linking Swisslog with
TrueTTY you have to
press the button
 .
TrueTTY will start if it was not running before pressing this button.
.
TrueTTY will start if it was not running before pressing this button.
When TrueTTY is launched a special toolbar is displayed in the QSO-Edit Window to trigger the TrueTTY macros. This toolbar is only visible while TrueTTY is running and hides automatically when TrueTTY is closed. It contains:
-
12 Buttons which send macro 1 thru 12 when pressed
-
a drop down list with all 36 available macros. Select a macro and double-click to send it
-
a TX-Button to start or stop the transmission
-
a Pause button which pauses or restarts the transmission.

TrueTTY works the same way as CWType with Macros. Please read this chapter
HamScope Operation
To start operating digital modes linking Swisslog with HamScope you have to
press the button
![]() . HamScope will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
. HamScope will
start if it was not running before pressing this button. After
some seconds you will see this button like this
![]() . The green
dot indicates that the DDE link has been established between Swisslog and
HamScope. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close HamScope Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between HamScope and Swisslog.
. The green
dot indicates that the DDE link has been established between Swisslog and
HamScope. While connected, if you press again this button you deactivate the
connection between both programs. Or if you close HamScope Swisslog will
automatically detect that the link has been broken. In both cases the button
will show again the red indicator. You can press again the button to start
the link between HamScope and Swisslog.
Deactivating the link by pressing the
![]() button can be
very useful in the following cases:
button can be
very useful in the following cases:
- you prefer to work SSB in Swisslog using the CAT functions of the DX Window but don't want to close HamScope
- you are working digital modes but alternating with SSB/CW in Swisslog and this option gives you more flexibility and fast changes to operate from one program to another
When you enter a callsign in HamScope automatically will be entered (not saved) in the QSO Entry window of Swisslog. You can enter a callsign in HamScope in 2 different ways:
- Manually entering a callsign and change cursor to another field
- If you have enabled the option Set the call in HamScope from SWISSLOG when a call is changed you can enter callsigns directly from Swisslog
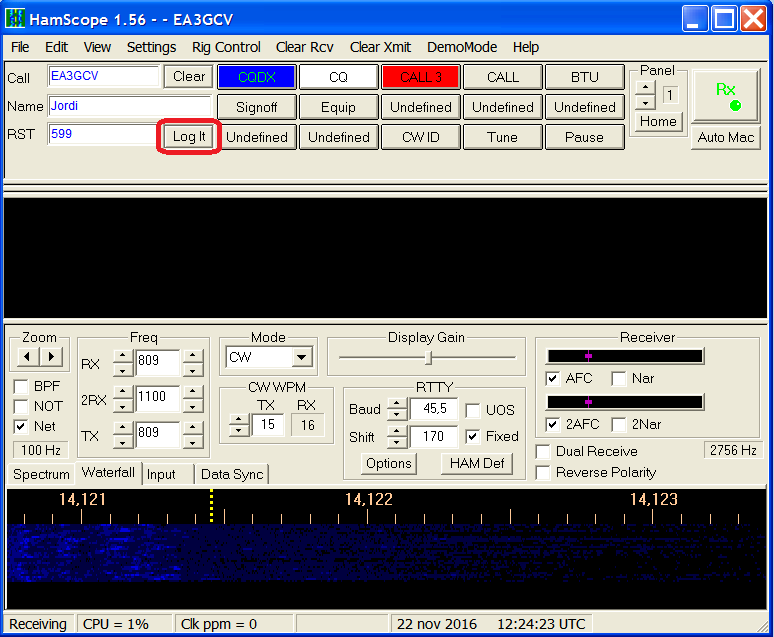
Swisslog reads from the following Hamscope fields:
- Callsign
- Name
- QTH
- Mode
- QRG (Rig Control window must be opened and Rig configured)
- RST sent
- RST received
If you press the HamScope button "Log it" the QSO will be saved in both Swisslog and HamScope. If you set the Set QSO Time on save option the QSO time will be set to the time when you press the save button. Otherwise the default behaviour is the following: the QSO Start time will be set when you enter the callsign and the QSO End Time will be set when you press the button "Log it".
If you press the HamScope button "Clear" all QSO fields will be cleared in both Swisslog and HamScope.
JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition Operation
VERY IMPORTANT:
- JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition version 4 or higher supports Swisslog. You will have to update it if you have an older version and want to use it along with Swisslog.
- SWISSLOG must be running first before using this program!
- If you are using Windows Vista or higher and SWISSLOG is installed in the Program Files folder, you MUST run HB9HQX Edition with full administrator privileges otherwise you will get an error. Right click in the HB9HQX icon and select "Run as administrator".
- JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition exchange information via TCP connection in localhost (127.0.0.1) through port 7802. In case of communication problems check that your antivirus/firewall is not blocking this port! If QSO is not saved in Swisslog after pressing the Save QSO button in HB9HQX Edition, you have to add a firewall exception to HB9HQX Edition to allow all incoming/outgoing connections.
Perform the following steps to configure Swisslog as logdatabase in JT65-HF HB9HQX Edition:
- Open HB9HQX and go to Configure | Pause and open configuration window.
- Select the LOG tab then the SWISSLOG tab. HB9HQX Edition will detect where Swisslog is installed.
- Press the TEST CONNECT button.
- If connection is succesful press the SAVE CONFIGURATION button:
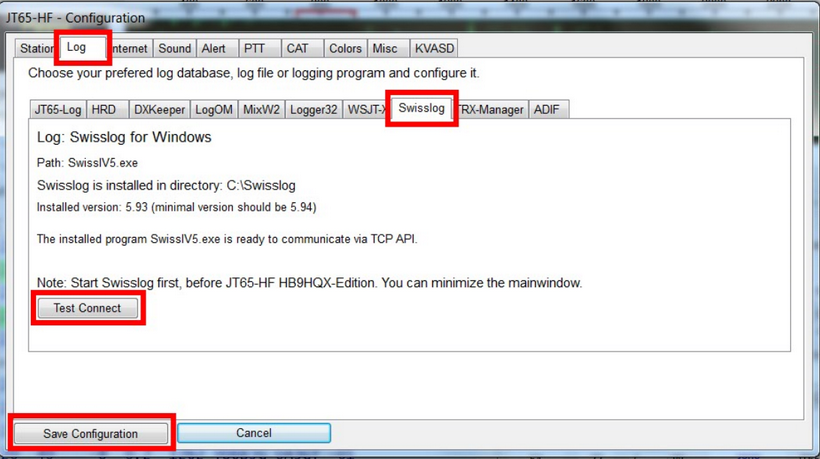
In the lower right part of the main window you will see "Swisslog (and version number)" as current Logdatabase and total number of JT65 QSOs stored in the Swisslog database. HB9HQX Edition loads all JT65 QSOs stored in Swisslog when connection is performed.
When QSO is finished simply press the LOG QSO button and QSO will be automatically saved in Swisslog:
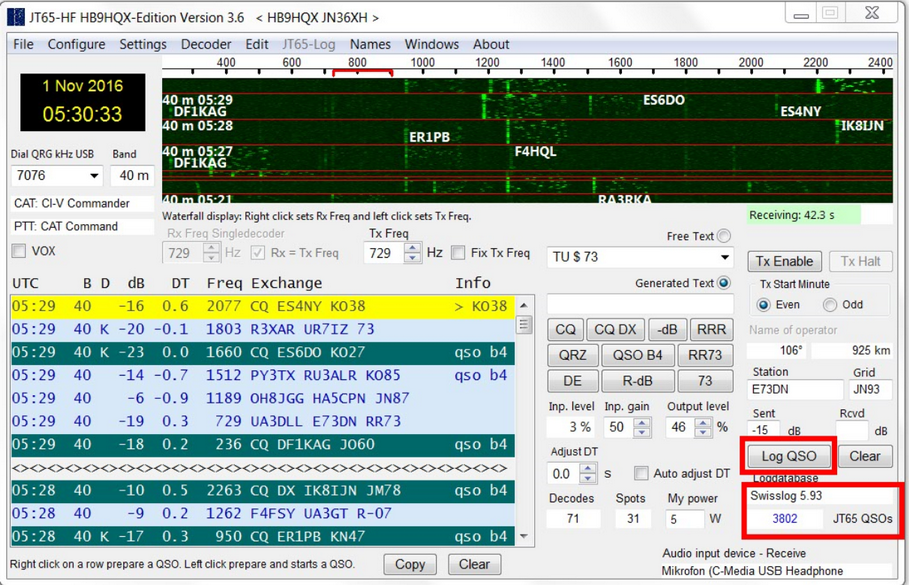
The following fields will be transferred to Swisslog:
-
Call
-
Name
-
Date
-
Start Time
-
End Time
-
Sent report
-
Received report
-
Grid
-
QRG
-
eQSL status (if eQSL realtime logging is used in HB9HQX, the L_eQSL_Status field in Swisslog will be set to "Uploaded" and the L_eQSL_Send_date will be also set)
-
Uploaded status to Club Log (if Club Log realtime logging is used in HB9HQX, the L_CLUBLOG_QSO_UPLOAD_STATUS field in Swisslog will be set to 1 and the L_CLUBLOG_QSO_UPLOAD_DATE will be also set).
-
TX Power (will be set in the Swisslog comments field as "TX Power:")
-
Comments
IMPORTANT: If you use the realtime logging options in Swisslog you have to disable the realtime logging in HB9HQX Edition, otherwise you will upload 2 QSOs at the same time!
Name and Grid fields will be checked in the selected Callbook databases in Swisslog (if configured). Name will only be checked if empty in HB9HQX. If QTH locator is set as 4 digit format in HB9HQX and found in Callbook databases in 6 digits format (being the same Maiden Head!), the 6 digits locator will be saved in Swisslog. Example:
-
JN93 is set in HB9HQX for current QSO. After checking in the selected Callbook database, Swisslog find a profile for this station with locator JN93AL. JN93AL will be saved in QSO instead of JN93.